
How low can the exchange rate fall? Will the Bank of England take measures to support the pound?
At the end of last week, bearish positions on the British pound sharply intensified. Traders seem to have tried to resist such a powerful downward movement until the last moment, but it did not work out. Events are developing in such a way that the pound in the future can not only update distant historical lows, but also risks setting a new anti-record.
The BoE's decision on the rate and the announcement of the interim budget, to put it mildly, did not impress the markets. The central bank raised the rate by only 50 bps, accumulating a backlog from the Federal Reserve. The new economic plan failed to allay investors' concerns about the approaching recession in the country.
The collapsed economic indicators were also another reason for short positions. The GfK consumer confidence indicator plunged to -49 from -41, updating the historical record. The last time such figures could be seen was in 1974. The CBI retail activity indicator fell to -20 in September from 37 in August.
Preliminary PMI estimates could not act as a kind of reassurance for the market. The composite index fell to 48.4 from 49.6 due to the deterioration in the service sector, where the corresponding indicator fell to 49.2 from 50.9.
At first, the GBP/USD pair fell to the area of 1.1020, which is the low since 1985. Then shorts intensified and the quote easily broke down the 1.0900 mark.
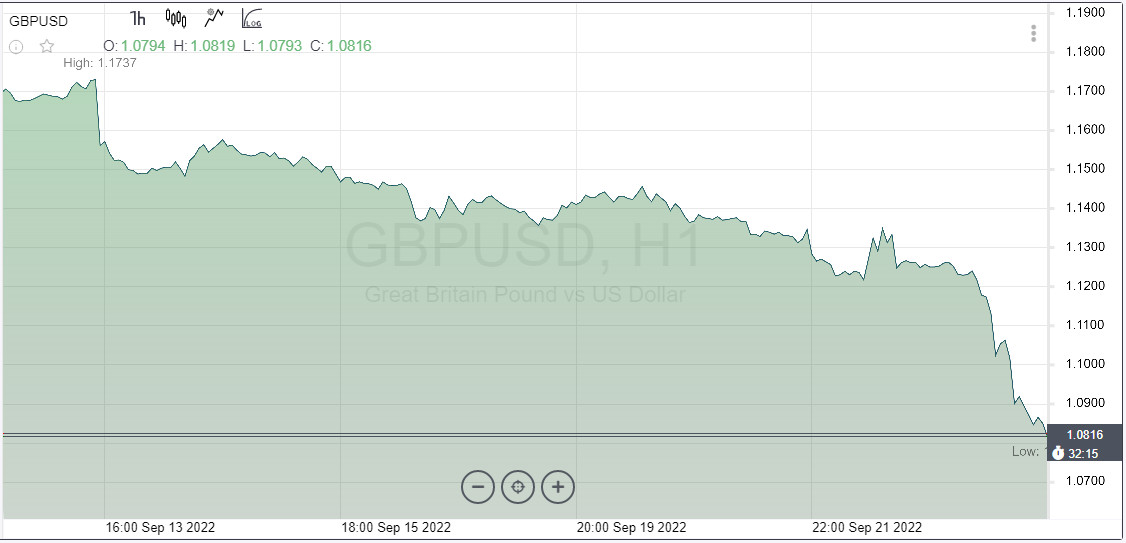
Since the beginning of the year, GBP/USD has lost approximately 20%. Given inflation of 10%, nervousness should be not only among market players, but primarily among the government and the BoE. If officials do step up their efforts to maintain the pound, volatility in the foreign exchange market risks being prohibitive or getting out of control.
What's Wrong with Government Measures?
The pound was mostly brought down by new government measures. The authorities have announced significant tax cuts since 1972 in an attempt to push the country's economic growth to 2.5%.
At least some, but actions and in theory, and even according to the government's plan, it was supposed to support the mood. However, investors have their own vision of the situation and they did not believe that the British authorities, led by Liz Truss, would be able to finance these measures without hindrance.
Radical changes to the tax code imply a reduction in the basic income tax rate from 20p to 19p from April 2023. The highest income tax rate has been reduced from 45p to 40p, while the increase in national insurance contributions this year will be canceled in November.
In addition, the planned increase in corporate tax has been postponed indefinitely. At the same time, Brits buying housing for the first time will be able to see a noticeable weakening of the state fee. The cost of all the announced tax cuts, according to the authorities, is 45 billion pounds.
At the same time, the government's decision to limit electricity bills will cost much more, approximately 130 billion pounds.
In general, this means that the British government will need to borrow more, increasing the supply of gold on the market.
What will Happen to the Pound?
The panic selling of the pound made many think about the future prospects of the British currency. What is it: a temporary turbidity and an excessively strong and completely unreasonable reaction of worried investors, or is the pound really on the path of a great crisis? Will there be parity with the dollar for the first time in history?
Indeed, the pound is now under the strongest pressure, including due to the incessant advance of the dollar. The fall of the pound coincides with the time when there was a significant sell-off on world markets. Even in normal times, this creates obstacles for the national currency of Britain.
Parity with the dollar is considered by analysts as an extreme measure, which is still far from reality. At the same time, new record lows are quite possible.
It is unlikely that government measures will lead to a collapse of the pound or create problems when selling gold coins.
"Given that the economy is flirting with recession, tax cuts supporting demand are not necessarily a bad idea. But this tax cut should be permanent, not temporary," Oxford Economics believes.
The pound is expected to continue to decline to about 1.0500 against the dollar in the short term. Meanwhile, the BoE will have no choice but to raise the size of the rate hike. At the November meeting, the central bank should increase the rate by 75 bps. Thus, the markets will raise the forecast for the maximum bank rate from 3% to 4%.
 English
English 
 Русский
Русский Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Bahasa Malay
Bahasa Malay ไทย
ไทย Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Български
Български Français
Français Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 বাংলা
বাংলা हिन्दी
हिन्दी Čeština
Čeština Українська
Українська Română
Română

