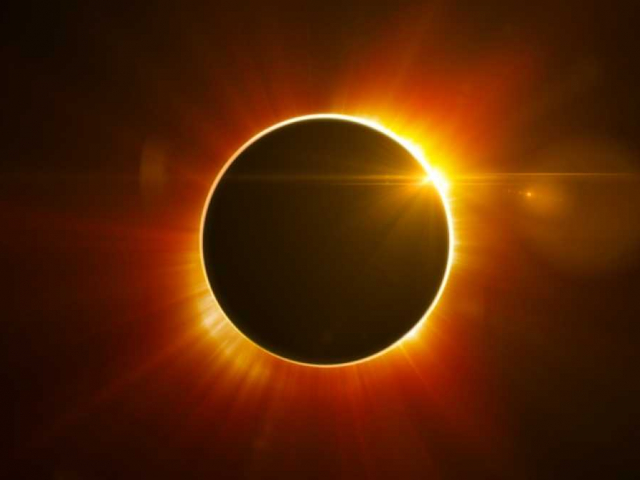

Total solar eclipse
A total solar eclipse is seen very rarely. It differs from the usual one which is observed several times a year. When a total solar eclipse occurs, the Moon blocks the Sun completely. It can be observed from the Earth. For the last time, the total solar eclipse was recorded in Novembers 2012. Scientists estimate it will not happen for the next 138 years.

The Transit of Venus
A transition is observed when Venus passes directly between the Sun and the Earth. Only a small portion of the solar-disc is covered. Venues looks like a tiny black dot moving across the Sun. The event repeats every 8 years. For the last 11o years, the planet runs along the same trajectory. The last transit of Venus was in 2012.
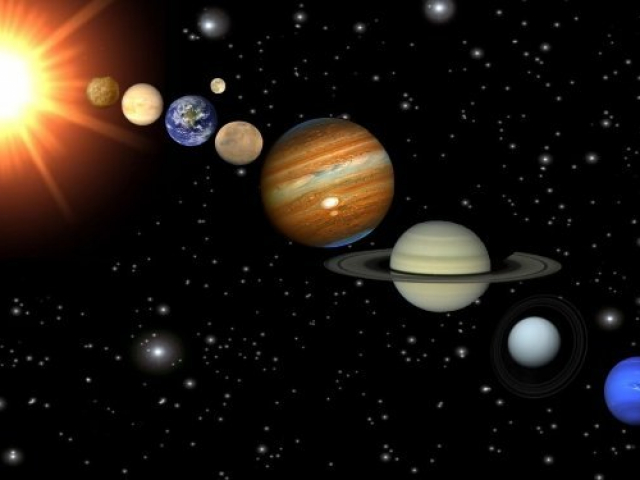
Planetary Alignment
The phenomenon is one of the rarest astronomical events. According to scientific research, the next alignment of celestial objects including Mars, Mercury, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn and the Moon will occur in 2040. The alignment of the five planets (Mars, Saturn, Venus, Mercury, and Jupiter) was recorded in 2000. The alignment of Jupiter, Mercury, and Venus happened in 2011.
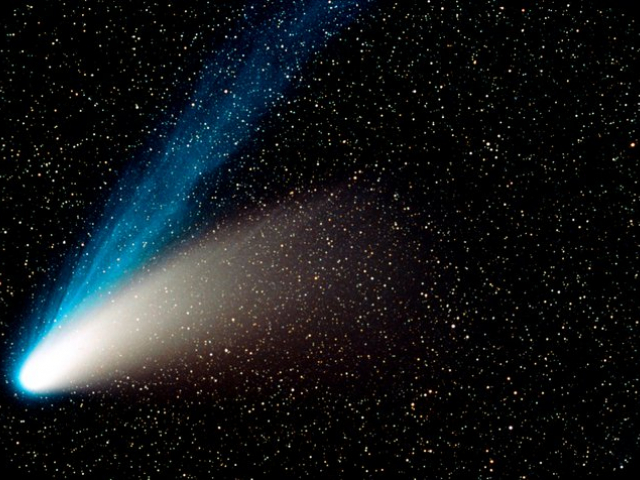

Comet ISON
Comet ISON, a sungrazing celestial body, is a unique event. It originated from the Oort cloud at the edge of the Solar System. Scientists consider it the brightest comet of the first half of the 19th century. It was discovered by two Russian astronomers on September 12, 2012. In November 2013, the comet split into two parts. According to estimated data, ISON flew 3.5 billion years before reaching the Sun. Its weight was constantly growing due to the accumulation of dust particles. The comet collapsed at a distance of 1 million km to the Sun.
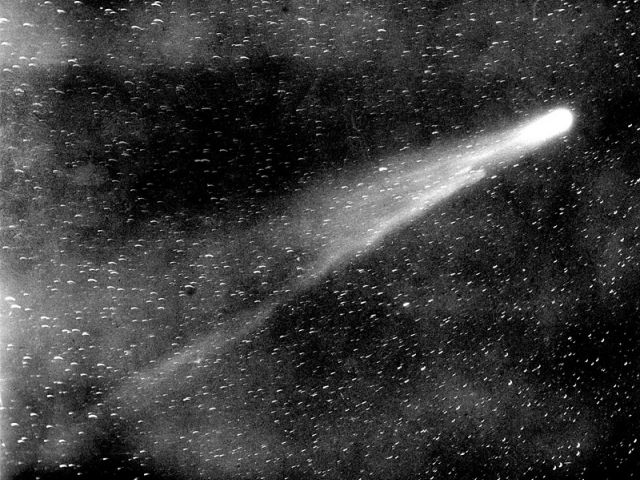

Halley’s comet
The periodic appearance of Halley's comet is the most interesting of the rare astronomical phenomena. It returns to the Sun every 75 years. The celestial body was named after the English astronomer Edmund Halley, who discovered it in 1531. The comet moves around the elliptical orbit. It is one of the brightest in the Solar System. Halley's comet is visible to the human eye. Its dimensions are 14 km long and 8 km wide. The last time the object passed near the Sun was in 1986, and the next appearance is expected in 2061.
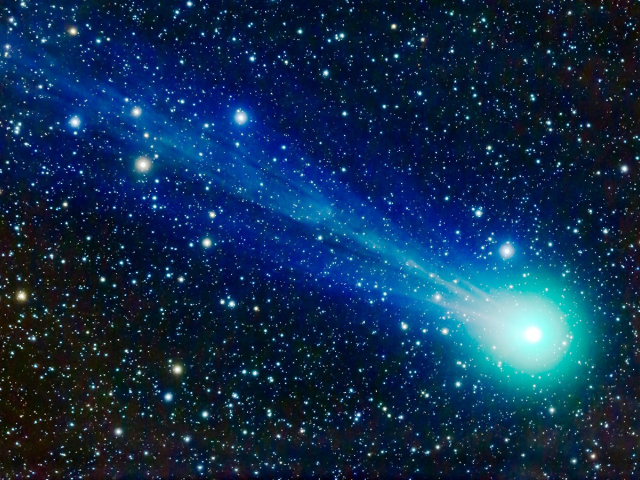

Comet Hale–Bopp
Experts consider the Hale-Bopp comet to be the brightest celestial body. It is 1000 times more intense than Halley's comet. The comet is visible from the Earth. It is estimated that the period of its circulation around the Sun is 2392 years. Comet Hale–Bopp was discovered by American astronomers Alan Hale and Thomas Bopp on July 23, 1995. Its closest distance to Earth is 193 million km. The comet movement is extremely difficult to predict. The orbit is constantly shifting, so it is not an easy task to foresee the flight path of the celestial body.
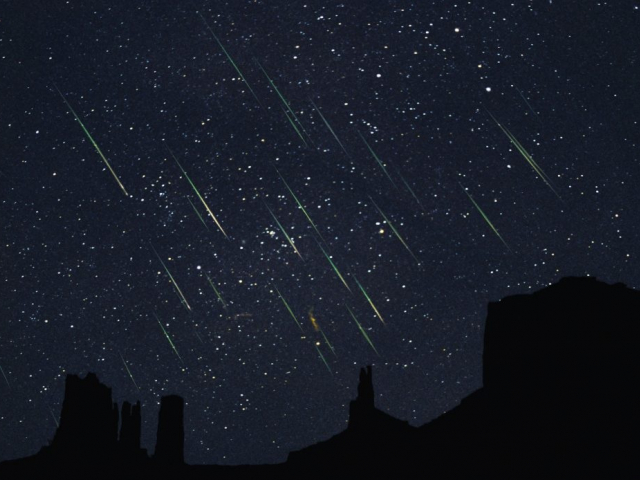

The Leonids
The Leonid meteor shower occurs at the intersection of the Earth and the orbit of Tempel-Tuttle comet. This spectacular meteor storms happens every 33 years. The Leonids are characterized by a huge number of meteors flying through the atmosphere. Their number reaches 100 thousand. The most powerful meteor storms were recorded in 1833.

67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
In comparison with Hale-Bopp comet, 67P/C–G‘s trajectory is more easily to predict. It travels around the Sun in six years. The comet was discovered in 1969. Its trajectory is under the gravitational influence of Jupiter. There are ice formations on the surface of 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko comet which turn into steam with dust particles as it approaches the Sun. The comet falls under the influence of Neptune’s gravitational force when passing near the planet.
 Български
Български 
 Русский
Русский English
English Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Bahasa Malay
Bahasa Malay ไทย
ไทย Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 বাংলা
বাংলা हिन्दी
हिन्दी Čeština
Čeština Українська
Українська Română
Română
